What does body weight regulation mean?
Body weight regulation refers to the complex biological systems that maintain relative stability in body weight over time. These systems involve energy intake, energy expenditure, and hormonal signals. While weight fluctuates naturally, the body works to maintain equilibrium around a regulated set point influenced by genetics, behavior, and environment.
How does nutrition influence energy balance?
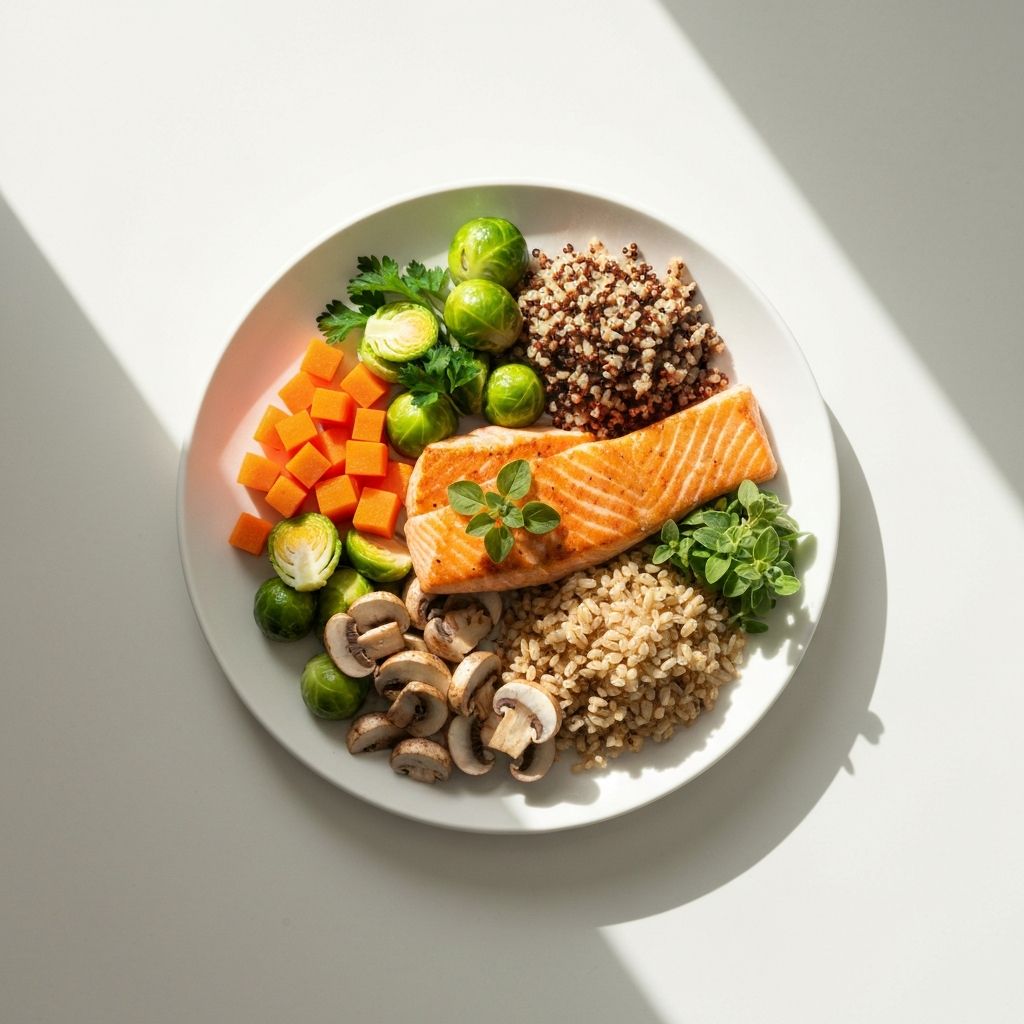
Nutrition affects energy balance through total energy intake and nutrient-specific effects. Different foods and macronutrients influence appetite, satiety, thermic effect, and subsequent eating patterns. Dietary composition, food volume, and nutrient density all play roles in how nutrition relates to energy homeostasis.
Does metabolism really slow with age?
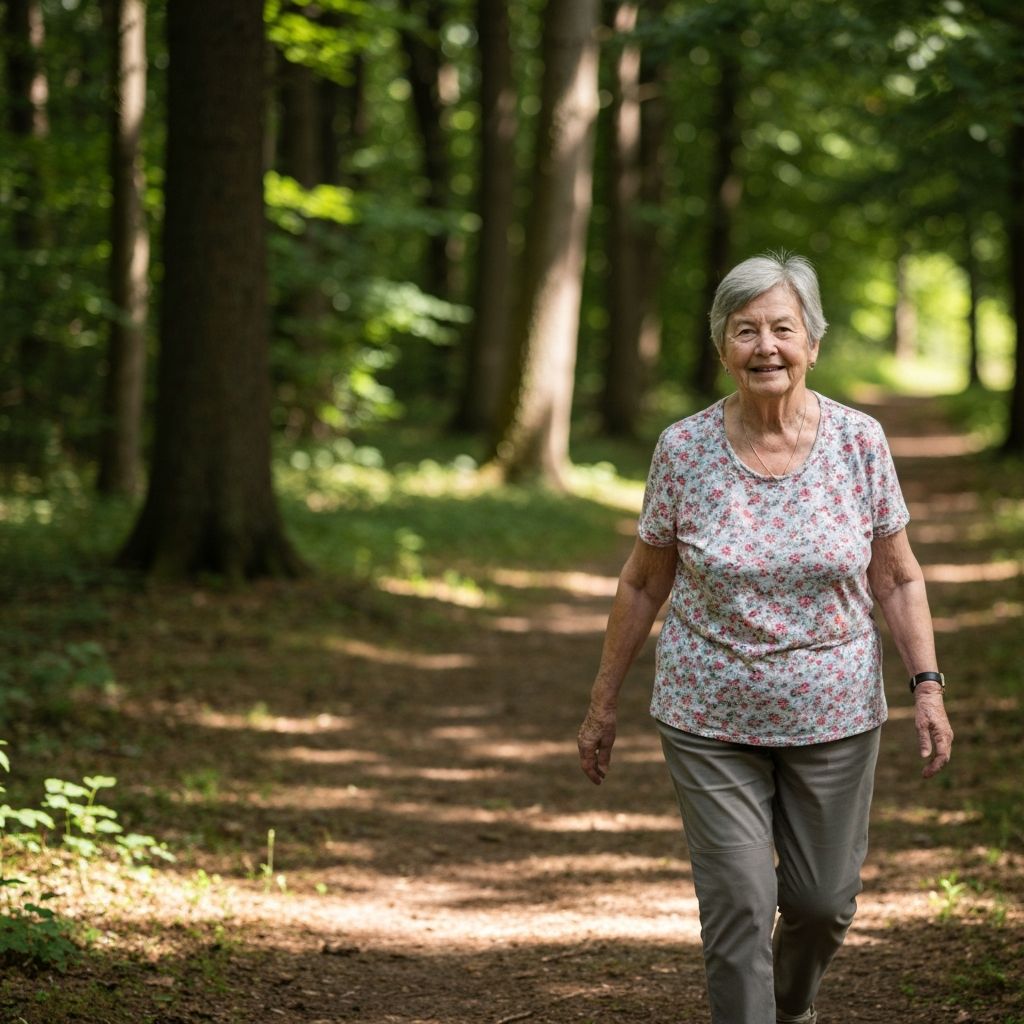
Metabolic rate does decline gradually with age, approximately 2-8% per decade after age 30. This decline relates primarily to loss of muscle mass and changes in body composition. Regular physical activity, particularly resistance training, can substantially moderate this decline.
What role does sleep play in weight regulation?
Sleep and circadian rhythm significantly influence appetite-regulating hormones, energy expenditure, and food intake patterns. Research indicates associations between insufficient sleep and altered appetite signals. Sleep quality and consistency appear relevant to metabolic function.
Are carbohydrates bad for weight management?
Weight management relates to total energy balance rather than specific macronutrients. Carbohydrates provide energy and different types affect satiety differently. Research shows that carbohydrate quality, quantity, and context within overall diet influence appetite and eating patterns.
How important is meal frequency?
Research suggests meal frequency is less critical than total daily intake and overall food quality. Some people feel more satisfied eating frequent small meals; others prefer fewer, larger meals. Individual preferences and satiety responses vary considerably.
Can exercise alone change body composition?
Exercise contributes to energy expenditure and can influence body composition, particularly when combined with resistance training for muscle maintenance. However, total energy balance fundamentally depends on both intake and expenditure. Exercise interacts with eating behaviors, which vary individually.
Is genetic background deterministic for body weight?
Genetic factors influence metabolism, appetite regulation, and body composition potential. However, environment, food choices, and activity levels substantially modify genetic predisposition. The interaction between genetic and environmental factors is complex; neither operates independently.
What is the basis for claims about "metabolism-boosting" foods?
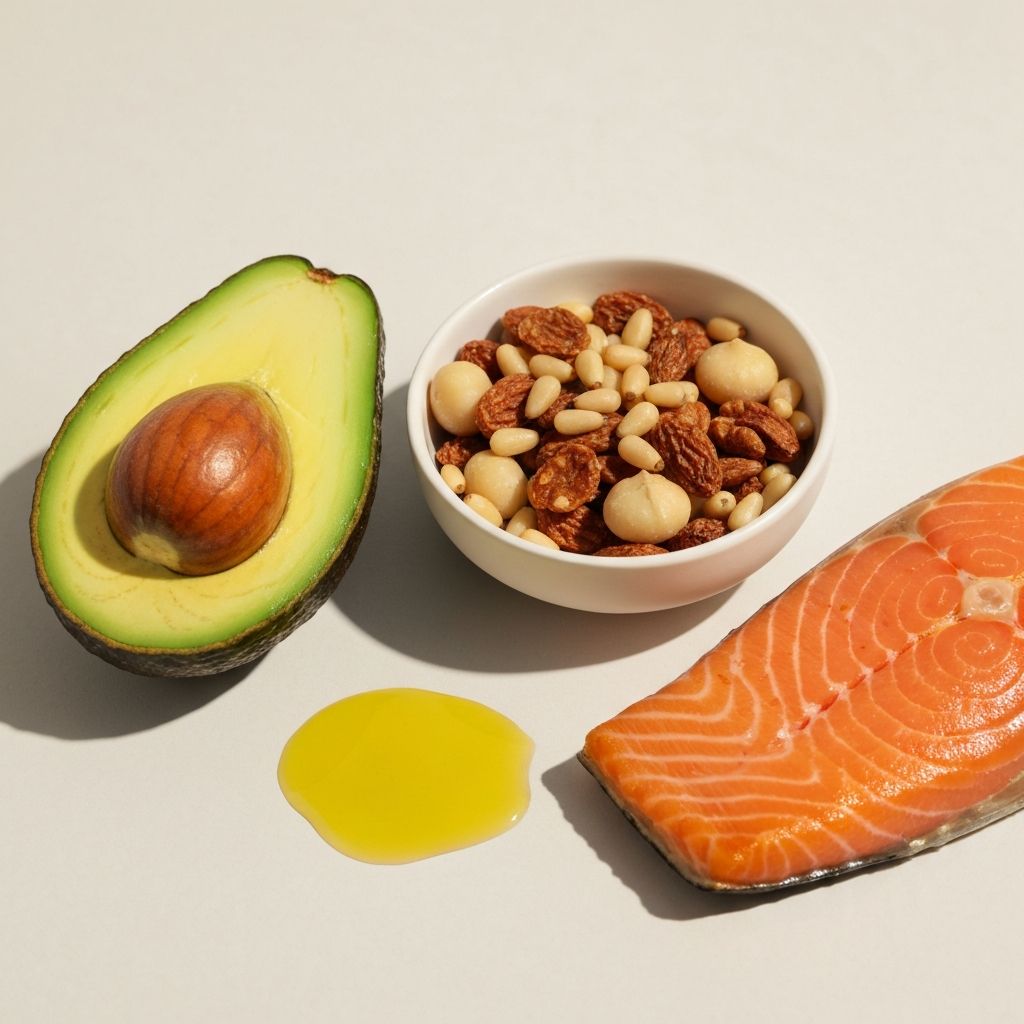
Different foods produce varying thermic effects—the energy required for digestion. Protein has a higher thermic effect than fats or carbohydrates. However, these differences are relatively modest. No foods produce dramatic metabolic increases. Total caloric intake remains the dominant factor in energy balance.